
#Bitdefender 2019 update license
A one-year, 10 device license features costs only $79.99 (£60.87).
#Bitdefender 2019 update plus
Bitdefender Antivirus Plus 2019: Priceīitdefender Antivirus Plus 2019 costs a fairly average $39.99 (£30.43) for the one device, single year license, but give some thought to the selection of plan for multiple Windows devices, and additional years to improve the value further.
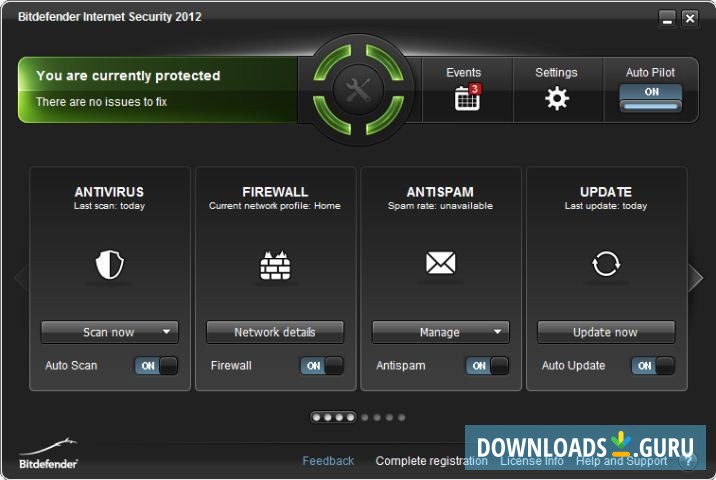
A dashboard sports a current clean interface on the Windows build to make use even easier. This works to plug the holes that malware uses to take advantage of the vulnerabilities on your device to launch further widespread attacks.įor these appreciate the “Set it and forget it” approach, Bitdefender's Autopilot system delivers useful, intelligent recommendations that optimize the protection to support the individual’s pattern of usage. No one else involved in creating, producing or delivering test results shall be liable for any indirect, special or consequential damage, or loss of profits, arising out of, or related to, the use or inability to use, the services provided by the website, test documents or any related data.įor more information about AV-Comparatives and the testing methodologies, please visit our website.Also of note is that the novel Network Threat interference. We do not give any guarantee of the correctness, completeness, or suitability for a specific purpose of any of the information/content provided at any given time. We take every possible care to ensure the correctness of the basic data, but a liability for the correctness of the test results cannot be taken by any representative of AV-Comparatives. AV-Comparatives and its testers cannot be held liable for any damage or loss, which might occur as result of, or in connection with, the use of the information provided in this paper. in whole or in part, is ONLY permitted after the explicit written agreement of the management board of AV-Comparatives prior to any publication. This publication is Copyright © 2019 by AV-Comparatives ®. No false alarms were encountered on the tested 500 legitimate online banking sites. Test Resultsīelow you can see the percentages of blocked phishing websites (size of test set: 509 phishing URLs). The set of legitimate online banking websites for the false alarm test consisted of 500 clean URLs (all of them using HTTPS and showing a login form) from all over the world. for PayPal, online banking & credit cards, e-mail accounts, Dropbox, eBay, social networks, online games and other online services. The phishing campaigns targeted various types of personal data, including login credentials etc. All phishing URLs had to be active/online at time of testing and attempt to get personal information. 509 Phishing URLs were tested as soon as we discovered them. The test took place between the 6 th June and 18 th June 2019. In our test scenario, we simulate the common situation where users rely on the anti-phishing protection provided by their security products while browsing the web (and/or checking their webmail accounts anti-spam features are not considered, as they are not within the scope of this test). The most recent product version of Bitdefender Internet Security available at time of testing has been used in this test.

Phishing is an example of social engineering techniques used to deceive users, and exploits the poor usability of current web security technologies.”įor more information about how not to get hooked by a phishing scam, please have a look at e.g. Phishing is typically carried out by e-mail spoofing or instant messaging and it often directs users to enter details at a fake website whose look and feel are almost identical to the legitimate one. Communications purporting to be from popular social web sites, auction sites, online payment processors or IT administrators are commonly used to lure the unsuspecting public. But the hook inside it takes the complete fish out of the lake.

This is similar to Fishing, where the fisherman puts a bait at the hook, thus, pretending to be a genuine food for fish. “Phishing is a way of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
